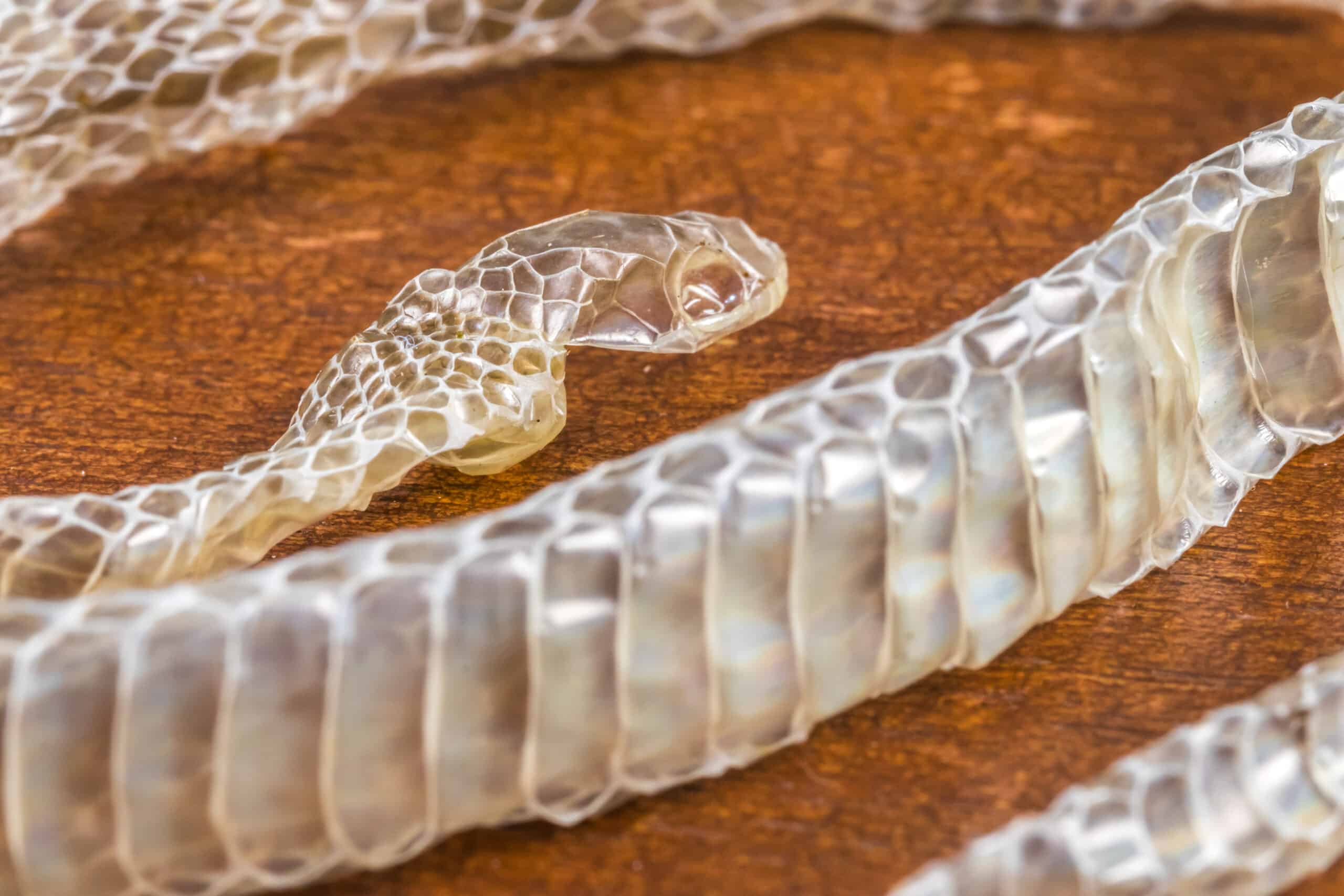
Exotic leather – the suffering of animals
Animal leather products are often created from the hide of cattle, sheep and goats. Every year, several million exotic animals are killed for exotic leather. Among them are reptiles such as snakes, crocodiles, alligators, lizards and ostriches. Their skin is then made into belts, watch straps, bags, purses, shoes or furniture covers.
Threat to endangered species
Many of the animals are raised on farms or ranching systems. Often the animals are also caught in the wild in Africa, America or Southeast Asia. For the ranching system, eggs are collected from wild crocodiles or alligators and then hatched on farms. Some of the young animals are released again, while the other part has to vegetate on farms to be killed at the age of one to three years.
The animals, some of which are caught illegally, are all declared as farm raised, so it is almost impossible to know where the skins actually come from. The trade of exotic animals, both illegal and legal, is fundamentally problematic because for many species there is no known knowledge about their population size. Thus, no conclusions can be made as to whether the species is at risk. For example, the exotic leather industry poses a significant threat to endangered species.
So the animals suffer
The different animals are killed in different cruel ways. Among other things, snakes are drowned, decapitated, the skull is crushed or they are pumped up with air until the resulting pressure causes the organs to burst or the animal suffocates. The process is similar for crocodiles. They are also pumped up with air until they die. Alternatively, their neck is cut open and then the spinal cord is removed, ultimately destroying the brain with a metal pin. Many of these processes result in animals still being alive when they are skinned in pain.
Pandemic risk
A report by the international Livestock Research Institute and the United Nations Environment Programme addresses the causes of zoonotic diseases. According to the study, about 60 percent of human diseases originate in animals. The mass keeping of animals is one of the factors responsible for the emergence of zoonoses. For the production of exotic leather, the animals are kept en masse in tiny enclosures. The hygiene conditions there are correspondingly poor. In this way, bacteria and viruses can spread and transfer quickly. It often happens that employees work without protective clothing and are also injured by the animals during the killing. Thus, these come into direct contact with the blood and offal of the animals.
What consumers can do
It’s always easier to dress vegan and sustainable. There are numerous synthetic and plant-based alternatives for leather, for which no animals have to die.